mail: Surgeon@bodybybatal.com
phone: (310) 230-5911

Gynecomastia
Introduction to Gynecomastia
Conveniently located to serve the areas of Beverly Hills and Tarzana, CA
For the treatment of enlarged breasts in men or “man boobs”.

Gynecomastia is an enlargement of the breasts in men that can affect one or both breasts at the same time and not always evenly. While regular liposuction can reduce the size of the breast through fat extraction, gynecomastia cannot be treated with liposuction alone. Generally, it isn’t a serious problem and doesn’t always affect a person’s physical health, but mentally the person may feel self-conscious.
Before and After Photos
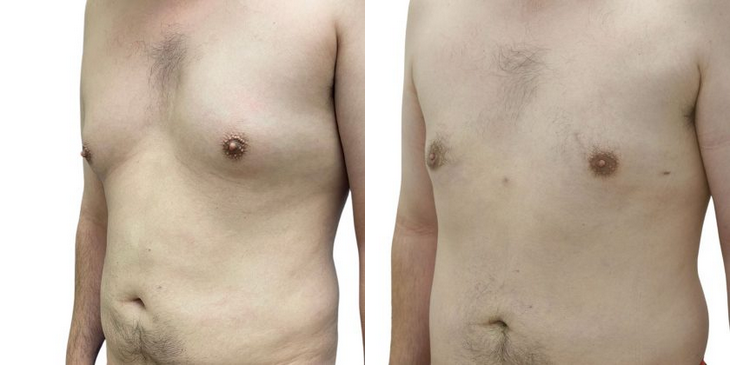
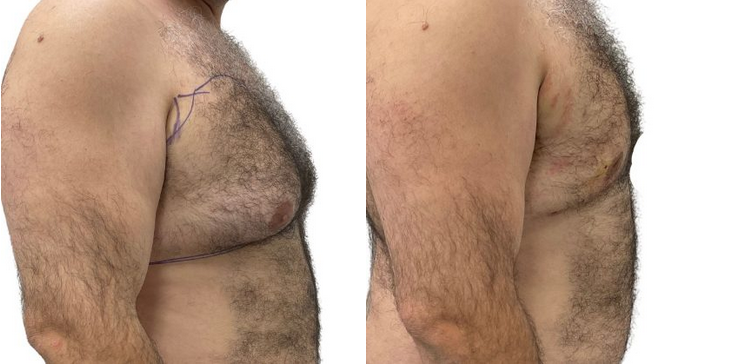
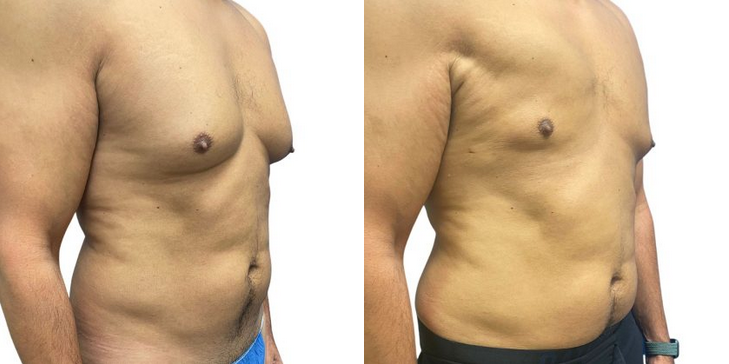
Dr. Batal's GynecomastiaTreatment
Treatment usually consists of liposuction of the breast tissue to reduce fat deposits in the chest and then removal of the enlarged glandular tissue. Previously, a small incision around the nipple would have been performed to remove the gland. In order to
avoid affecting the sensitivity of the nipple post-op, Dr. Obaida Batal uses specialized instruments inserted through the same small incisions used for liposuction to trim down and remove the enlarged gland. This method is less invasive and the small incisions heal quicker.
Understanding Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. It is a relatively common occurrence, particularly among teenagers. Studies have shown that up to 65% of boys may experience some degree of gynecomastia during adolescence. Thankfully, this condition often resolves on its own within two years, with around 90% of cases resolving by the age of 17 or 18.
Although gynecomastia is usually benign and does not typically pose significant health risks, it can cause psychological distress and affect self-esteem in affected individuals. Therefore, it is crucial to address the issue and explore treatment options when necessary.
When considering treatment for gynecomastia, it is essential to distinguish between surgical and non-surgical approaches. Non-surgical options often involve managing underlying health conditions that may contribute to breast tissue enlargement. For example, if gynecomastia is caused by obesity, weight loss through a combination of healthy eating and regular exercise can help reduce breast tissue size. Furthermore, certain medications, such as those for hypertension or psychiatric disorders, may contribute to gynecomastia as a side effect. In such cases, adjusting or changing medication under a doctor’s supervision could alleviate the symptoms.
In conclusion, gynecomastia is a common condition in teenagers, with the majority of cases resolving on their own within two years. Non-surgical approaches, including managing underlying health issues and making changes to drug use, can be successful methods in treating gynecomastia. It is important for teenagers and their caregivers to consult a healthcare professional to discuss options and determine the most suitable course of action.
What causes gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of the male breast glandular tissue, which can occur due to various causes including hormone imbalances and certain medications. Fluctuations in testosterone and estrogen levels during puberty and aging can lead to gynecomastia.
During puberty, hormonal changes occur which may cause a temporary increase in estrogen levels relative to testosterone. This hormonal imbalance can result in the development of breast tissue in males. Similarly, aging can also lead to an increase in estrogen levels due to decreased testosterone production, leading to the development of gynecomastia.
Certain medical conditions can also contribute to gynecomastia. For example, conditions that affect the testes, pituitary gland, or adrenal glands can cause hormonal imbalances. Conditions such as hypogonadism, hyperthyroidism, and liver disease can disrupt the testosterone-estrogen balance and result in gynecomastia.
Moreover, several medications have been associated with gynecomastia. Spironolactone, a diuretic, can block the effects of testosterone and lead to the development of breast tissue. Calcium channel blockers, used to treat high blood pressure and heart conditions, can interfere with hormonal signaling pathways, resulting in gynecomastia. Additionally, medications used in the treatment of prostate cancer, like certain anti-androgen therapies and estrogens, can also cause gynecomastia.
In conclusion, gynecomastia can be caused by hormone imbalances during puberty, aging, and certain medical conditions. Additionally, specific medications can contribute to the development of gynecomastia. Understanding the various causes of gynecomastia is crucial in order to provide appropriate treatment and support for individuals affected by this condition.
What are the symptoms of gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, primarily caused by an imbalance of hormones. The primary symptom of gynecomastia is breast enlargement, which is usually symmetrical and located around the nipple. The affected breast tissue may have a rubbery or firm feel to it.
It is crucial to differentiate gynecomastia from male breast cancer. Unlike gynecomastia, male breast cancer presents with hard or firm breast tissue, nipple retraction, and the enlargement of underarm lymph nodes. These symptoms are not typically observed in gynecomastia.
In addition to breast enlargement, other potential signs and symptoms of gynecomastia may include breast tenderness, nipple discharge, swollen nipples, and the presence of psychological or emotional concerns. Breast tenderness may lead to discomfort or pain in the breast area. Nipple discharge, although uncommon, can occur and may be clear, yellow, or bloody in color. Swollen nipples may be an indication of gynecomastia, as they can become more prominent due to the enlargement of the breast tissue. Finally, individuals with gynecomastia may experience psychological or emotional concerns, such as feelings of embarrassment, self-consciousness, or anxiety related to their enlarged breasts.
In summary, the symptoms of gynecomastia mainly revolve around breast enlargement, typically symmetrical around the nipple with a rubbery or firm feel. Other potential signs include breast tenderness, nipple discharge, swollen nipples, and psychological or emotional concerns. It is important to differentiate gynecomastia from male breast cancer by noting the specific symptoms associated with each condition
How is gynecomastia diagnosed?
Gynecomastia is diagnosed through a combination of methods, including a physical exam, medical history review, blood tests, ultrasound, and mammogram.
The first step in diagnosing gynecomastia is a thorough physical examination. During the exam, the doctor will evaluate the breast tissue by feeling for any abnormalities or changes in size and texture. They will also assess the patient’s overall health and look for any signs of other underlying conditions that may be causing the breast enlargement.
In addition to the physical exam, the doctor will review the patient’s medical history. This includes asking about any medications or supplements the patient is taking, as some can cause gynecomastia. They will also inquire about any symptoms the patient is experiencing, such as pain or tenderness in the breast area.
Blood tests are commonly used to help diagnose gynecomastia. These tests can measure hormone levels, such as testosterone and estrogen, which play a role in breast tissue development. An imbalance in these hormones may contribute to the development of gynecomastia.
If the physical exam and blood tests are inconclusive or if the doctor suspects an underlying condition, they may order additional imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or mammogram. These tests can provide detailed images of the breast tissue and help identify any abnormalities or masses.
In summary, diagnosing gynecomastia involves a physical exam, medical history review, blood tests, and potentially additional imaging tests. These methods help evaluate breast tissue, hormone levels, and identify potential underlying causes. It is important for individuals who suspect they may have gynecomastia to seek medical evaluation for an accurate diagnosis.
How is gynecomastia treated?
Gynecomastia, the development of excess breast tissue in males, can be treated using different approaches depending on its classification as either physiologic or pathological.
Physiologic gynecomastia is commonly observed in newborns, adolescents, and older men due to hormonal imbalances. In most cases, no specific treatment is required as the condition usually resolves on its own within six months to two years. However, reassurance and regular monitoring are important to ensure proper regression.
On the other hand, pathological gynecomastia occurs due to underlying medical conditions or medications that disrupt hormone balance. In these cases, the treatment should be directed towards addressing the underlying cause. This may involve stopping or replacing medications or treating the underlying disease. In certain cases, medication such as tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors may be prescribed to reduce breast tissue growth.
In cases where gynecomastia persists beyond two to three years or causes significant psychological distress, surgical treatment may be considered. Surgery typically involves the removal of excess breast tissue through liposuction or surgical excision, depending on the extent of tissue growth. Post-surgical recovery may involve pain management, wound care, and wearing a compression garment to aid in healing.
In conclusion, the treatment options for gynecomastia depend on its classification as physiologic or pathological. Physiologic gynecomastia often resolves naturally, while pathological gynecomastia requires addressing the underlying cause. Surgical treatment may be considered in cases that persist beyond two to three years or cause significant distress.
The Gynecomastia Procedure
The Gynecomastia Procedure is a surgical intervention specifically designed to address the condition of gynecomastia, which is characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. This procedure aims to reduce and reshape the male chest, restoring a more masculine appearance. Gynecomastia can often cause self-consciousness and emotional distress in affected individuals, leading them to seek corrective measures. With advancements in surgical techniques and technologies, the Gynecomastia Procedure has become a safe and effective solution, providing men with the opportunity to regain their self-confidence and enhance their overall body image. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the Gynecomastia Procedure, including its indications, the surgical process, recovery, and potential risks and complications. By gaining a better understanding of this procedure, individuals considering gynecomastia surgery can make informed decisions about their own well-being.
Liposuction for Gynecomastia
Liposuction for gynecomastia is a procedure aimed at addressing the issue of enlarged male breasts. Gynecomastia is the medical term for the development of excess breast tissue in males, which can lead to self-consciousness and a loss of confidence. Liposuction offers an effective solution by removing the excess fatty tissue, resulting in a more masculine chest contour.
The procedure begins with the application of anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort throughout the surgery. Then, a small incision is made in the targeted area, often near the armpit or along the edge of the areola. Through this incision, a thin tube, known as a cannula, is inserted. The cannula is connected to a suction machine that gently removes the excess fatty tissue.
By specifically targeting the fatty tissue in the chest area, liposuction allows for the reduction of breast size without the need for more invasive surgical techniques. This makes it an ideal option for many men with gynecomastia, as it minimizes scarring and reduces the recovery period.
After the procedure, patients are required to wear a compression garment to support the chest and help with the healing process. The results of liposuction for gynecomastia are generally long-lasting, provided that the patient maintains a healthy lifestyle and does not experience significant weight fluctuations.
In conclusion, liposuction for gynecomastia is a cosmetic procedure that involves the removal of excess fatty tissue through a small incision. It is an effective way to reduce the appearance of enlarged male breasts and restore confidence in those affected by gynecomastia.
Direct Gland Excision for Gynecomastia
Direct Gland Excision is a surgical procedure performed to address gynecomastia, a condition characterized by the excessive growth of glandular tissue in the male breast. This procedure aims to remove the excess glandular tissue to achieve a more masculine chest appearance.
During the surgery, an incision is made on the lower half of the areola. This location allows for optimal access to the glandular tissue, while also minimizing the visibility of resulting scars. The size of the incision may vary depending on the extent of tissue and skin reduction required. In cases where there is significant excess tissue, larger incisions may be necessary to ensure thorough removal. However, for individuals with minimal excess glandular tissue, smaller incisions may be sufficient.
Following the excision of the glandular tissue, the incision is closed using sutures, and dressings are applied. It is common for patients to experience some post-operative swelling and bruising, which gradually recede over time.
While Direct Gland Excision is generally considered safe and effective, there are potential complications that patients should be aware of. One possible complication is an uneven chest contour, which may occur if the removal of glandular tissue is not symmetrical. Reduced nipple sensation is another potential complication, although it is usually temporary.
In summary, Direct Gland Excision is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of excess glandular tissue to treat gynecomastia. The incision and scar size will vary depending on the extent of tissue and skin reduction required. Patients should be aware of potential complications such as uneven chest contour and reduced nipple sensation.
Skin Tightening with Radiofrequency for Gynecomastia
Radiofrequency (RF) treatment is a non-invasive technique used for skin tightening in the treatment of gynecomastia, a condition characterized by the enlargement of male breast tissue. This procedure offers several benefits, including minimal discomfort, no scarring, and a quick recovery period.
The RF treatment works by heating the deep layers of the skin, stimulating collagen production and tightening the skin. This technique can effectively reduce breast gland tissue, resulting in an improved appearance of the chest. RF treatment is particularly useful for individuals with mild to moderate gynecomastia.
The procedure involves the use of a handheld device that emits RF energy into the targeted area. The specialist performing the treatment will guide the device over the chest area, ensuring comprehensive coverage. The heat generated by the RF energy stimulates collagen synthesis, which gradually tightens the skin and reduces breast gland tissue.
RF treatment is considered safe and effective, with minimal risks and side effects. Patients may experience mild redness or swelling immediately after the procedure, but these typically subside within a few hours. The treatment can be repeated as necessary to achieve the desired results.
In conclusion, radiofrequency treatment is a non-invasive procedure that effectively tightens the skin and reduces breast gland tissue in individuals with gynecomastia. With its numerous benefits, minimal discomfort, and quick recovery time, RF treatment offers a safe and effective solution for improving the appearance of the chest.
Gynecomastia Recovery
Gynecomastia recovery is a gradual process that involves post-surgery care, adherence to specific instructions, and closely monitoring any potential complications. After the surgery, it is important to follow the surgeon’s recommendations for care to ensure optimal recovery.
The timeline of gynecomastia recovery varies from person to person but typically takes about 4-6 weeks. During the initial stage, patients are advised to rest and avoid strenuous activities for at least a week. It is crucial to avoid any movements that may strain the chest area.
To aid in the recovery process, surgeons often recommend wearing compression garments for a specified period. These garments help reduce swelling, support the chest tissue, and promote proper healing. They should be worn as instructed, usually for several weeks, to achieve the desired results.
While complications are rare, patients should be vigilant and watch for signs of infection, excessive bleeding, or abnormal swelling. It is important to promptly report any concerns to the surgeon to ensure swift intervention if required.
Expected outcomes of gynecomastia surgery include a flatter, more contoured chest, improved self-confidence, and a better quality of life. The precise results and recovery timeline may vary based on individual factors such as the extent of the surgery and the body’s natural healing process.
Adhering to the surgeon’s instructions is crucial to achieve the desired outcomes and minimize any potential complications. It is essential to avoid engaging in rigorous physical activities, especially those that put strain on the chest muscles, during the recovery period. Following the prescribed restrictions helps prevent undue stress on the healing tissues and allows for optimal recovery.
In conclusion, gynecomastia recovery involves adhering to post-surgery care instructions, monitoring for complications, and following restrictions on physical activity. Adhering to the surgeon’s guidelines and wearing compression garments as recommended play a vital role in achieving the expected outcomes of a flatter and contoured chest. Monitoring for any complications ensures timely intervention if necessary.
Gynecomastia Recovery for Dr. Batal
A minimum of 5-7 days of downtime is needed for the initial recovery. A follow-up after a week is needed to remove any exterior sutures as well as to check on the overall healing process from the procedure. Patients will be required to wear compression garments 24/7 for the first few days to reduce swelling and promote healing. Mild bruising will also be noticeable for the first 1-2 weeks. Most patients can return to work or normal routine within 1-2 weeks after surgery buy full recovery may take up to a month.
Gynecomastia Result
Gynecomastia, also known as enlarged male breasts, is a condition that affects a significant number of males. This condition is characterized by the overdevelopment of breast tissue in males, resulting in an enlarged appearance of the chest. The outcomes or results of gynecomastia can vary from person to person, but they generally have both physical and psychological effects.
Firstly, gynecomastia is often a result of an imbalance in hormone levels, particularly an increase in estrogen and a decrease in testosterone. This hormonal imbalance can occur due to various reasons, including puberty, aging, certain medical conditions, medication use, or drug and alcohol abuse. As a result, males with gynecomastia may experience physical changes such as increased breast size, tenderness or sensitivity in the breasts, and in some cases, the nipple area may become puffy or swollen.
Aside from the physical changes, gynecomastia can also have psychological effects on males. Enlarged breasts can lead to feelings of embarrassment, low self-esteem, and body image issues, causing individuals to avoid certain activities or social situations. This condition can also impact their overall quality of life and relationships.
In conclusion, gynecomastia is a condition that can have significant outcomes on males. The effects of hormone imbalance and the resulting physical changes can lead to both physical and psychological challenges for individuals with gynecomastia. It is important to address this condition with proper medical guidance and support to alleviate the impact it has on individuals’ well-being.
Gynecomastia Cost
Gynecomastia, the enlargement of male breast tissue, can cause physical and emotional discomfort for many individuals. The cost of gynecomastia treatment varies depending on several factors.
Firstly, the type of procedure chosen contributes significantly to the cost. There are generally two types of procedures available: liposuction and excision surgery. Liposuction involves removing excess fat through small incisions, while excision surgery entails the removal of glandular tissue, excess skin, or both. Excision surgery tends to be more expensive as it is a more complex procedure.
Hospital fees are another cost factor to consider. The type of facility and its location can impact the price. Typically, larger hospitals in urban areas have higher fees compared to smaller clinics. Additionally, the necessary use of medical equipment and resources during the procedure can drive up costs.
Anesthesia fees are also a consideration. The type of anesthesia used, such as local anesthesia or general anesthesia, can affect the overall cost. General anesthesia, often preferred for more extensive procedures, tends to be more expensive due to the involvement of an anesthesiologist.
Consultation fees are an essential part of gynecomastia treatment. Professionals spend time assessing the patient’s condition, discussing treatment options, and providing the necessary information before the procedure. These fees can vary depending on the experience and reputation of the specialist.
Lastly, post-operative care costs should be accounted for. This includes medications, follow-up appointments, and any necessary garments or compression vests for optimal healing and recovery. These costs may vary based on individual requirements.
Understanding the various factors that contribute to the cost of gynecomastia treatment can assist individuals in planning for this procedure effectively. Consulting with a trusted medical professional is vital to obtain accurate information about the total expenses involved.
Conclusion: Gynecomastia
In conclusion, diagnosing gynecomastia can be effectively accomplished by following the algorithm provided in the background information. This algorithm outlines the necessary steps to evaluate and determine the presence of gynecomastia in male patients.
The findings of this algorithm involve a thorough assessment of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and the possibility of performing relevant blood tests, mammogram or ultrasound, and further tests if needed. The importance of physical examination in diagnosing gynecomastia cannot be overstated. It allows clinicians to assess the size and characteristics of the breast tissue enlargement, as well as any associated signs such as asymmetry or nipple discharge. This examination can help differentiate true gynecomastia from other conditions that can mimic its appearance.
Blood tests, including hormone level assessment, can provide insights into potential underlying causes of gynecomastia. Additionally, mammogram or ultrasound imaging may be recommended to evaluate the breast tissue for any suspicious findings, such as tumors or cysts. These imaging modalities can aid in ruling out other diseases or pinpointing possible causes of gynecomastia. In some cases, further tests like tissue biopsy or MRI may be necessary for definitive diagnosis.
Overall, following this algorithm and considering each element of the diagnostic process is crucial in accurately diagnosing gynecomastia. It ensures that appropriate investigations are conducted to determine the cause and guides clinicians in providing appropriate care and treatment for affected individuals.
